The Saudis have joined other Asian countries in ditching their long-term sensitivity to the gold price. Evidence suggests the Saudi central bank has been covertly buying 160 tonnes of gold in Switzerland since early 2022, contributing to the current gold bull market.
Although the Saudis played a key role in the birth of the global dollar standard in the early 1970s, this time around they might even become a lynchpin for its dissolution.
Introduction
Until recently, Saudi Arabia’s gold demand would decline when the gold price went up and strengthen when the price went south. This dampened volatility in the gold market, which was ruled by the West for many decades.
Ever since the West immobilized Russia’s dollar assets in February 2022, those with diplomatic disagreements with the West are increasingly exchanging their dollars for physical gold. Saudi Arabia is the latest country—after China and Thailand—of which I have found cross-border trade statistics showing it has shifted from being price sensitive to a price driver.
As the chart above reveals, when the gold price went up (2016, 2017, 2019, and 2020), the Saudis cut back imports or became net exporters. Since 2022, however, the gold price has escalated, yet Saudi Arabia continued to import gold.
During the entire rally from late 2022 until the present, the Saudis have been a constant net importer which has boosted the gold price. The icing on the cake is that part of the flow into Saudi Arabia, the gold coming from Switzerland actually goes to the Saudi central bank, aka the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA).
Exposing Saudi Central Bank’s Hidden Gold Buying
Formally, any country’s cross-border gold trade statistics refer to “non-monetary” metal, meaning privately owned. Monetary gold—owned by central banks—is exempt from being disclosed in trade numbers. As I have demonstrated in a previous article, though, the non-monetary gold crossing the Chinese border is often a shipment heading for the vaults of the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) regardless.
Among industry insiders, SAMA is known for having accelerated secret gold purchases since 2022. By comparing the World Gold Council’s (WGC) estimates of total central bank buying (based on field research), to what central banks report to have bought to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), we can conclude that “unreported” purchases went through the roof starting in 2022. People familiar with the matter, but who prefer to stay anonymous, told me this is largely due to the PBoC, and to a lesser extent SAMA. That’s clue number one.
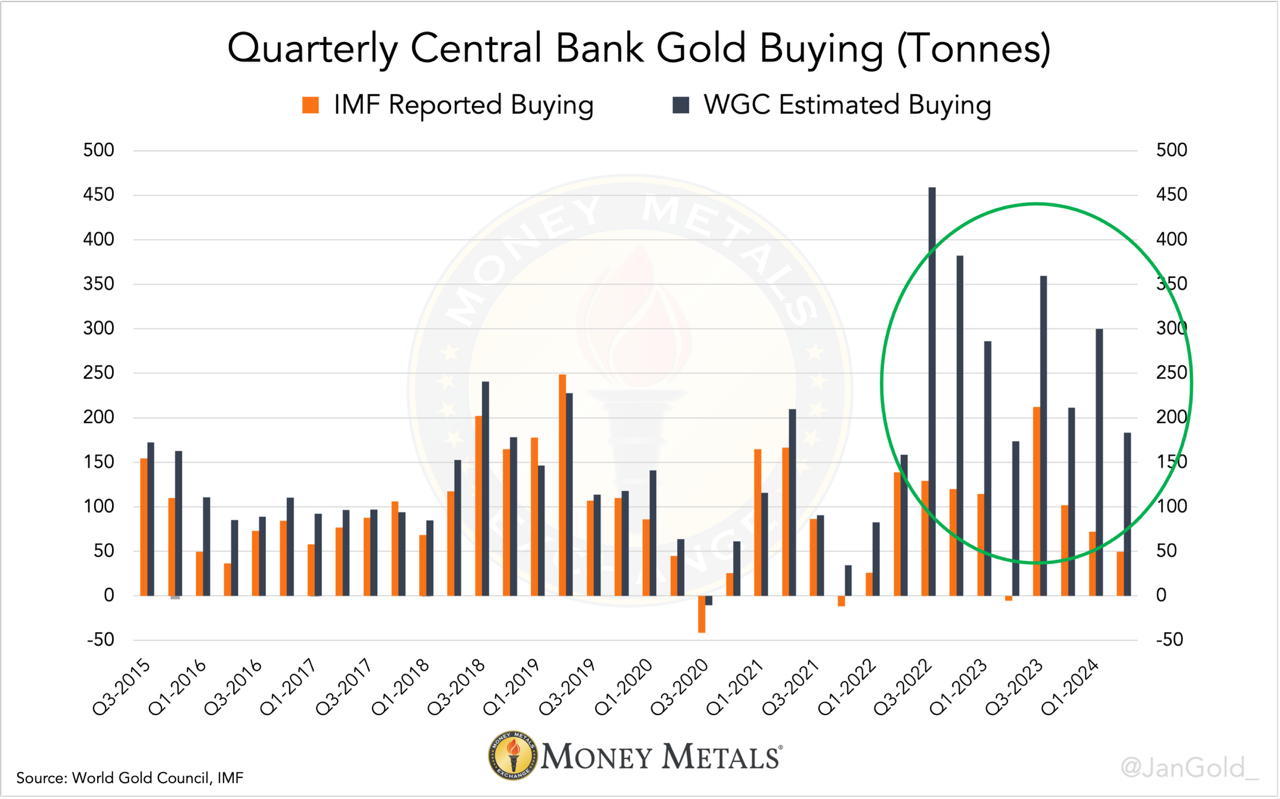 The gap between WGC and IMF data reflects unreported purchases.
The gap between WGC and IMF data reflects unreported purchases.
Because gold Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) hardly exist in Saudi Arabia, we can estimate SAMA purchases by comparing net imports to local consumer demand. Not coincidentally, net imports began to consistently outpace consumer demand in the second quarter of 2022, right after the Ukraine war started. SAMA was (and is) in a hurry to get its hands on physical gold.
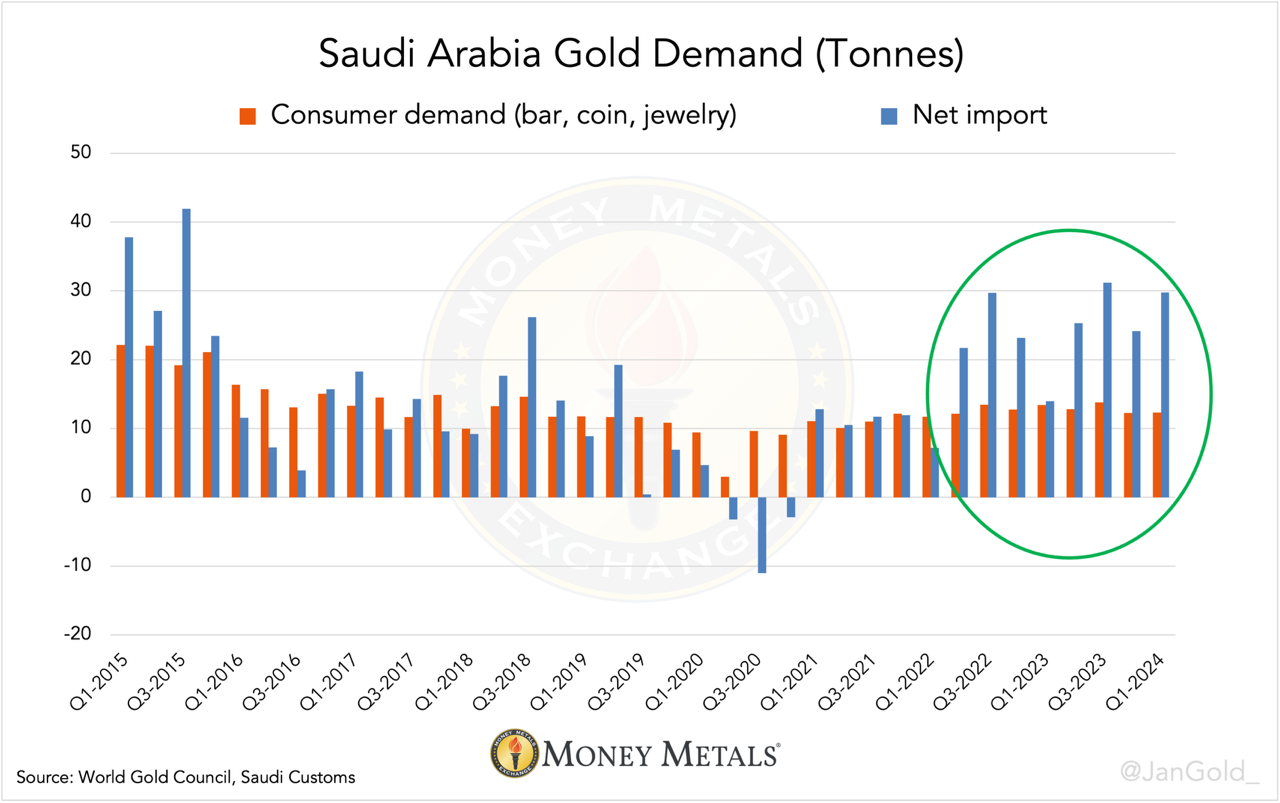 Discrepancies between consumer demand and net imports can also arise from dealer inventory changes and scrap supply, data that is unfortunately not publicly available.
Discrepancies between consumer demand and net imports can also arise from dealer inventory changes and scrap supply, data that is unfortunately not publicly available.
A source once told me that central banks often buy gold in Switzerland and London and have bullion banks pack and ship the gold to wherever the central banks want. This way it shows up in cross-border trade data because the bullion banks have to deal with customs.
Switzerland Pinpointed as Ground Zero for Secret Purchases
To find out if SAMA shops for gold bars in the Swiss Alps, I subtracted Saudi consumer demand from its net imports and compared the outcome (gold imported but not sold to consumers) to gross exports from Switzerland to Saudi Arabia. The result shows a strong match since Q2 2022, confirming SAMA has quietly been buying gold in Switzerland.
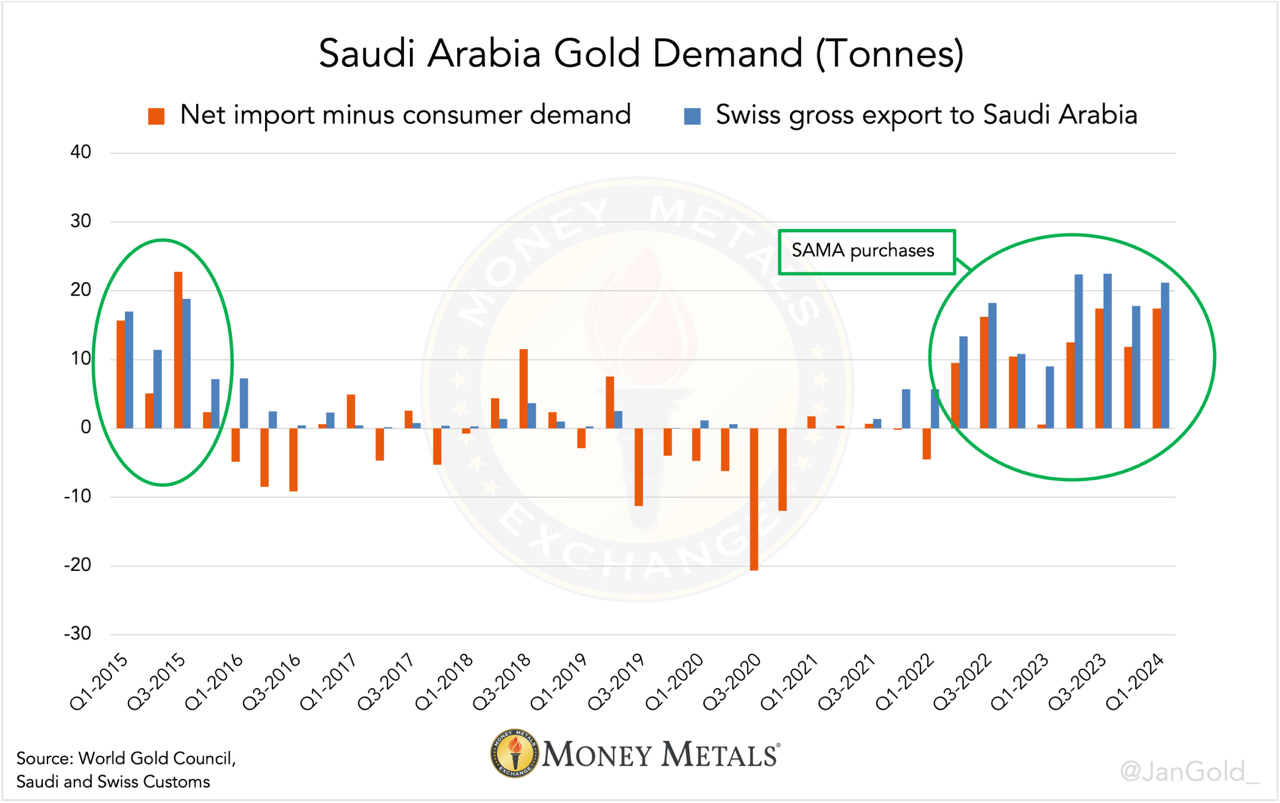
Any differences between the blue and orange bars are mainly due to scrap supply, a draw on net imports, which likely was substantial in 2020.
Saudi Arabia Owns Way More Gold Than It Wants Known
The data suggests SAMA bought approximately 160 tonnes of gold in recent years (and it was likely also bought in 2015 in Switzerland). How much it holds in total is unknown to me, partly because Saudi gold trade data only started in 2015. What happened before that is up for grabs. Neither do I know how much additional gold SAMA might be buying elsewhere.
One thing is for certain: Saudi Arabia owns much more gold than it wants the world to believe.
The last time the Saudi central bank updated its official gold reserves was in February 2008, when it conveyed to hold 332 tonnes, which was 180 tonnes more than in January 2008. Obviously SAMA didn’t buy 180 tonnes in one month.
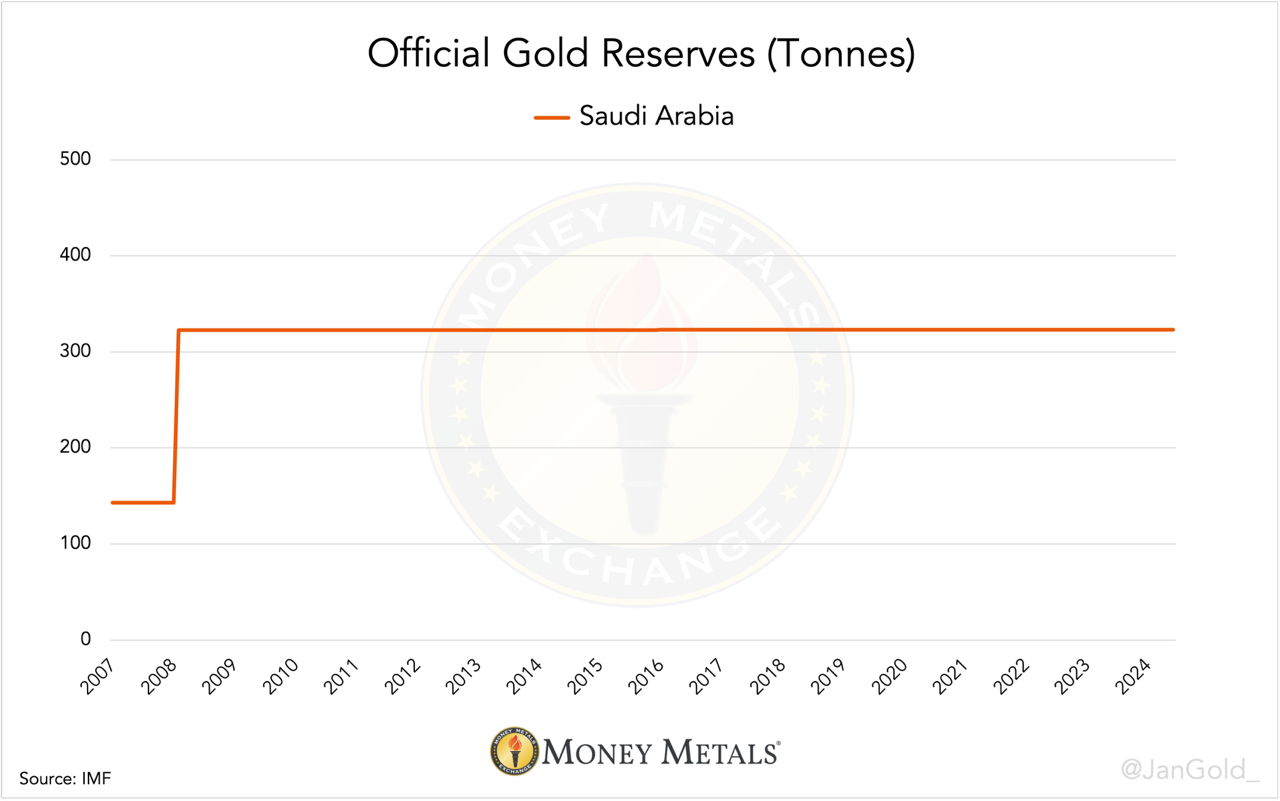
Past and current data indicate Saudi Arabia’s central bankers do not report changes to their gold holdings in a timely fashion. What will their next bulk update show?
Just like the reported gold reserves by the PBoC, the number put out by SAMA is purely political. By hiding how much precious metal the nation truly owns, the House of Saud avoids openly upsetting the United States.
But the evolution of countries in Asia storing more and more of their trade surpluses in gold—a time-tested neutral and sanction-proof reserve asset—is clear. Next to 160 tonnes by SAMA, I calculate the PBoC bought 1,600 tonnes since the war in Ukraine. Both central banks, the former of the most influential country in the oil market and the latter of the second largest economy globally, must be confident in what direction the gold market is headed.
How the above ties into other concerted initiatives by Asian nations to bypass the U.S. dollar, will be discussed in the next article.
Read the full article here








Leave a Reply